Projects
Subtle Motor Impairments in PD
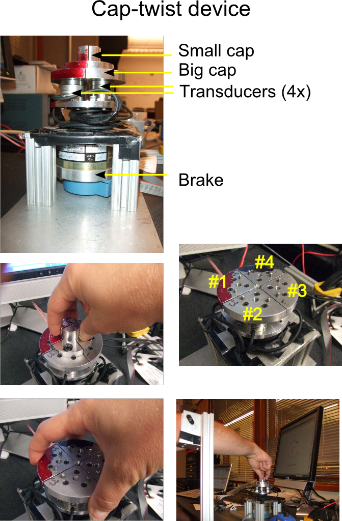
The goal of this research is to examine deficits in fine motor control, especially force control in individuals with Parkinson disease (PD). Projects related to this goal used multiaxial force sensors to unmask subtle deficits in force control that may not be evident on clinical examination, in individuals with early Parkinson disease, especially in the presence of a secondary cognitive task. Deficits in force control in early PD are also being examined for their association with disease severity.
Funding:
- University of Pittsburgh, Department of Physical Therapy
- Foundation for Physical therapy – Promotion of Doctoral studies II scholarship-2007
- Advanced Rehabilitation Research Training fellowship- NIDRR training grant # H133P080008.
Conference abstracts:
- Pradhan, S.D., Brewer B., Carvell G., Sparto P.J., Delitto A., Matsuoka Y., Force tracking characteristics in adults with Parkinson’s disease using a robotic devise: a case series: Platform presentation at Combined Sections Meeting (CSM) (Annual American Physical Therapy Association [APTA] conference) at the Gossman Graduate seminar-2007
- Pradhan, S.D., Brewer B., Carvell G., Sparto P.J., Delitto A., Matsuoka Y., Fine Motor Control and its Relation to Disease Progression in Individuals with Parkinson’s disease: Platform presentation at CSM (Annual APTA conference) at the Gossman Graduate seminar-2008
- Pradhan, S.D., Brewer B., Carvell G., Sparto P.J., Delitto A., Matsuoka Y., Relation between fine motor impairment and function in individuals with PD: Interactive and Podium Sessions at the International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, Kyoto, Japan – 2009
- Pradhan, S.D., Scherer, R., Matsuoka Y., Kelly V., Preliminary results for the use of sensitive devices to assess the effect of medication on attentional demands of precision and power grips in individuals with Parkinson’s disease: Platform presentation at the Future Trends in Rehabilitation Robotics Workshop held in conjunction with the 3rd IEEE International conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics, Tokyo, Japan -2010
- Pradhan, S.D., Kelly V., Effect of medication on attentional demands of precision and power grips in individuals with Parkinson’s disease: Platform presentation at CSM (Annual APTA conference) at the Neurology section – Degenerative disease SIG, New Orleans. -2011
Publications:
- Brewer B.R., Pradhan S.D., Carvell G.E., Delitto A., Feature selection for classification based on fine motor signs of Parkinson’s disease. Proceedings of the 31st Annual International IEEE EMBS Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Sept 2009, pg. 214-217.
- Pradhan S.D., Brewer B.R., Carvell G.E., Sparto P.J., Delitto A., Matsuoka Y, Relation between fine motor impairment and function in individuals with PD: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, June 2009, pg. 885-892.
- Scherer R., Pradhan S.D., Dellon B, Kim D, Klatzky R, Matsuoka Y, Characterization of multi-finger twist motion toward robotic rehabilitation: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, June 2009, pg. 812-817.
- Brewer B.R., Pradhan S.D., Carvell GE, Sparto PJ, Josbeno DA, Delitto A, Application of Modified Regression Techniques to Validate a Quantitative Assessment for the Motor Signs of Parkinson’s disease: Transactions on Neural Systems & Rehabilitation Engineering, Dec 2009, 17(6), 568-575. PMID: 19884100
- Brewer B.R., Pradhan S.D., Preliminary investigation of test-retest reliability of a robotic assessment for Parkinson’s disease. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2010;1:5863-6.
- Pradhan S.D., Brewer BR, Carvell GE, Sparto PJ, Delitto A, Matsuoka Y, Assessment of Fine Motor Control Using Force Tracking with a Secondary Cognitive Task in Individuals with Parkinson’s disease: J Neurol Phys Ther. 2010 Mar;34(1):32-40. PMID: 20212366
- Pradhan S.D., Scherer R, Matsuoka Y, Kelly VE. Use of sensitive devices to assess the effect of medication on attentional demands of precision and power grips in individuals with Parkinson disease. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2011 Oct;49(10):1195-9. PMID: 21748396
- Bowen L.K., Hands G.L., Pradhan S.D., Stepp C.E. “Fundamental Frequency Variability in Parkinson’s Disease”, J Med Speech Lang Pathol. 2013 Sep;21(3):235-244. PMID: 25838754
- Pradhan S.D., Scherer R., Matsuoka Y., Kelly V.E. Grip force modulation characteristics as a marker for clinical disease progression in individuals with Parkinson’s disease – a case-control study: Phys Ther. 2015 Mar;95(3):369-79 – Special Issue on Innovative Technologies for Rehabilitation. PMID: 25476717
Gaming & Virtual Reality
The goal of this research is to examine the role of simultaneous physical and cognitive challenge during exercise in individuals with early Parkinson disease. Projects related to this line of research have included (1) studies examining the efficacy of gaming interventions compared to traditional exercise for individuals with Parkinson disease (2) creating a free game description website for clinicians for efficient game selection for rehabilitation to promote knowledge translation in the area of active video gaming: kinectingwithclinicians.com
Funding:
- Royalty Research Fund- University of Washington, 2013-2015
- Institute of Translational Health Sciences – Pilot Grant program-2013-2014
Conference abstracts:
- Pradhan, S.D., The use of a gaming device for multimodal intervention in individuals with Parkinson disease: Poster presentation at CSM (Annual APTA conference), San Diego -2013.
- Deol J., Pradhan, S.D., Game therapy improves walking ability in individuals with Parkinson disease – Co – author & faculty mentor. Presenter – Jasjit Deol: Poster presentation at CSM (Annual APTA conference), Anaheim, CA, -2016
- Pradhan, S.D., Multimodal cognitive and physical exercise for individuals with mild Parkinson disease: Poster presentation at IV STEP, Ohio state university-2016
- Pradhan, S.D., Moritz C., Enriched environments for exercise in Parkinson’s disease: Poster presentation at PTWA conference, Tacoma, WA-2016
- Wessbecher L., Pradhan, S.D., Clinical characteristics of responders versus non responders to a gaming intervention in individuals with Parkinson’s disease (PD) – Poster presentation- CSM (Annual APTA conference), New Orleans, LA, Student Presenter – Laura Wessbecher-2018
- Levac D, Glegg SM, Fox EJ, Pradhan SD, Espy D, Deutsch JE, Virtual reality/active video gaming use and learning needs among physical and occupational therapists practicing in the US. Poster presentation- CSM (Annual APTA conference), Washington DC, Presenter – Danielle Levac-2019
- Levac D., Glegg S., Pradhan SD, Fox E., Espy D.,Chicklis E., and Deutsch JE, A comparison of virtual reality and active video game usage, attitudes and learning needs among therapists in Canada and the US, International Conference on Virtual Rehabilitation, Tel Aviv, Israel-2019.
Publications:
- Levac D., Espy D., Fox E., Pradhan SD., Deutsch J., ‘Kinect-ing’ with clinicians: A knowledge translation resource to support decision-making about video game use in rehabilitation: Phys Ther. 2015 Mar;95(3):426-40 – Special Issue on Innovative Technologies for Rehabilitation. PMID: 25256741
- Levac D., Pradhan S.D., Espy D., Fox E., Deutsch J. Usability of the ‘Kinect-ing with Clinicians’ website: A knowledge translation resource supporting decisions about active video game use in rehabilitation. Games Health J. 2018 Sep 4. doi: 10.1089/g4h.2017.0159. PubMed PMID: 30179519.
- Pradhan S.D., The use of commercially available games for a combined physical and cognitive challenge during exercise for individuals with Parkinson disease – a case report: Physiotherapy Theory and Practice: 2019 Apr;35(4):355-362. PMID: 29521568
- Levac D., Glegg S., Pradhan SD, Fox E., Espy D.,Chicklis E., and Deutsch JE., “A comparison of virtual reality and active video game usage, attitudes and learning needs among therapists in Canada and the US,” IEEE Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Virtual Rehabilitation (ICVR), Tel Aviv, Israel, 2019, pp. 1-7. DOI: 10.1109/ICVR46560.2019.8994624
Physical activity in PD
The goal of this research is to examine physical activity levels and strategies to improve physical activity in individuals with Parkinson disease. Projects related to this research have (1) used wearable commercial activity monitors to quantify physical activity levels in this population,(2) examined strategies to improve physical activity in this population with the help of stakeholder input: IDEASforPD website
Funding:
- Institute of Translational Health Sciences -Rising Stars Program – 2015-2017
- Patient Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) – Pipeline to proposal initiative – Tier 1-2016-2017
- Patient Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) – Pipeline to proposal initiative – Tier 2-2017-2018
Conference abstracts:
- Pradhan, S.D., Kelly V., Use of mobile technology to study physical activity levels and its diurnal variation in an individual with Parkinson disease – a case report: Poster presentation at CSM (Annual APTA conference), San Antonio, TX-2017
- Pradhan, S.D., Kelly, V., The use of a commercial physical activity (PA) monitor to quantify physical activity levels in individuals with Parkinson disease (PD) – Platform presentation – Degenerative disease special interest group – CSM (Annual APTA conference), New Orleans, LA-2018
- Pradhan SD, Beidler P, Chambers G, Hanson D, Harold P, Keiffer J, Initiating Discussions to Enhance physical Activity promotion Services for individuals with PD (IDEAS for PD) – Annual PCORI conference, Washington DC, -2018
- Roskoff M, Kelly VE, Fogelberg D, Pradhan SD, Relation between physical activity and sleep in individuals with Parkinson Disease. Poster presentation- CSM (Annual APTA conference), Washington DC, Presenter – Martin Roskoff (DPT3)-2019
- Thomas S, Pradhan SD, Predicting levels of walking related light activity (WRLA) for individuals with Parkinson’s Disease. Poster presentation- CSM (Annual APTA conference), Washington DC, Presenter – Sarah Thomas (Rehab Sci PhD Program)-2019
- Prusynski R., Fogelberg D, Kelly VE., Pradhan SD, Sleep Deficits and Their Association with Increased Sedentary Behavior for People with Parkinson’s Disease, Platform presentation- CSM (Annual APTA conference), Denver CO, Presenter – Rachel Prusynski (PhD student-Rehab Sci PhD Program)-2020
- Jewell S, Pradhan SD, Variability in Interday Physical Activity in Individuals with Parkinson’s Disease Compared to Healthy Older Adults, Poster presentation- CSM (Annual APTA conference), Denver CO, Presenter – Sam Jewell (SPT-DPT 3)-2020
Publications
- Pradhan S, Kelly VE. Quantifying physical activity in early Parkinson disease using a commercial activity monitor. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2019 Sep; 66:171-175.